Origination is the foremost stage of lending services that every individual must go through to obtain a loan, like a personal loan, business loan, home loan, auto loan, etc. Origination is a multi-step process, ranging from application and underwriting to disbursal of funds. Loan origination steps vary by loan type, lender policy, and multiple types of loan risk.
Every loan type will have different approval processes and criteria that can be manual and automated. The loan origination process can be paper-based or digital. The digital process includes the entire gamut of the loan origination process with minimal paperwork.
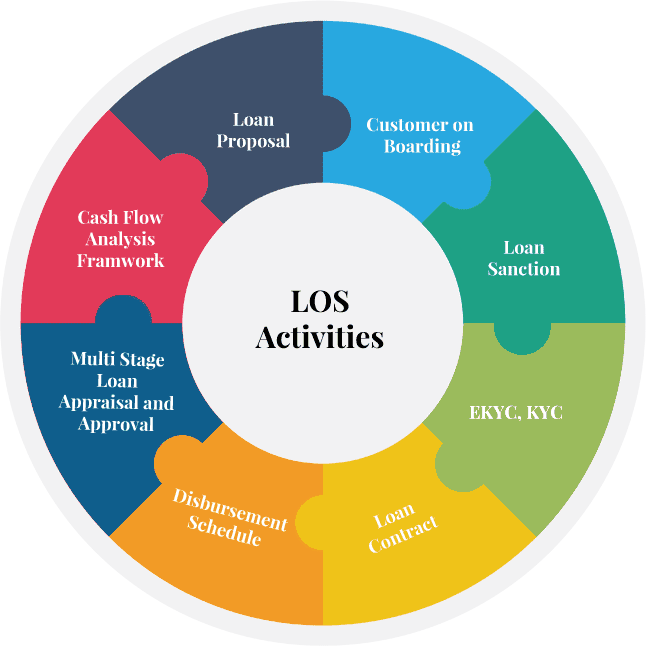
The loan origination process can be divided into seven main steps as follows:
1. Pre-qualification process
Pre-qualification is the first step in the loan origination process. Loan applicant supplies information to the lender or the third party like identity/ address details, current employment details, income, payment history, tax returns and expenses, and loan amount required. Based on the provided information and available loan options, the lender pre-approves the loan and makes an offer, allowing the borrower to continue.

For example, Rohit Bansal wants to get a home loan to buy a house worth Rs. 30 lakh. He applies for the loan online to know the amount and interest rate thereon he is eligible for. The lender requests basic information about his income and existing debts. Based on the details, the lender says Rohit is eligible for a loan of Rs. 25 lakh. He must submit documents and undergo more approval processes.
2. Documentation
The second stage of the loan origination process is documentation. The borrower needs to complete the application process by submitting relevant documents to substantiate income, employment, financial status and other credentials. The borrower can submit the documents online through the lender’s website or mobile app, or alternatively visit the nearest branch of the lender to submit hard copies.
3. Application processing
After receiving the application, the credit department reviews it for accuracy and completeness. If any error is spotted in the application or the applicant has not provided all information required, the credit analyst gets in touch with the loan applicant to procure the required missing information.
Lenders generally use Loan Origination Software (LOS) to assess the loan application. Depending on the algorithms employed by a lender, a sophisticated LOS can automatically flag files with missing fields and share it with the borrowers to complete it.
4. Underwriting process
The underwriting process plays a decisive role in the approval of a loan application. The lender evaluates the loan application against a number of criteria such as credit score, risk score, debt to income ratio, and repayment capacity. Some lenders also check the digital footprints of the loan borrower. The underwriting process is sometimes fully automated with the help of a business rules engine and API integrations in the loan origination system. In a business rules engine, lenders can include underwriting guidelines specific to products.
5. Credit decision
Based on the result of the underwriting process, the loan application is approved, declined or sent back to the originator to procure additional information. A rejection may be reconsidered if there are certain changes in parameters, such as reduced loan amount, increased loan tenure or revised interest rates to lower installments.
This step can also be automated with a rules engine for a degree of predictability. Even minor changes in the parameters, such as interest rates, tenure and loan amount, can be implemented into the system without coding.
6. Quality check
Consumer lending is tightly regulated in India. Regulations require lenders to maintain standards relating to capital adequacy, cash reserve ratio, credit ceiling, KYC norms, etc. Hence, the quality control step is critical to lending institutions. The loan application is sent to the quality control queue for auditing to ascertain full compliance with internal and external rules and regulations. This is essentially the last review of the application before disbursal. Quality control helps the lenders to avoid any lawsuit and disciplinary action in case of a dispute.

7. Loan Funding
Most consumer loans are disbursed once the loan documents are signed. Business loan, line of credit and second mortgage loans may take additional time for legal and compliance reasons. Lender issues a check or demand draft, which you can receive from the bank branch or is couriered to your address. In some cases, the loan amount can be credited to your bank account through NEFT.
Automation of loan origination process
As mentioned earlier, consumer lending is tightly regulated in India. Legislative reforms make it increasingly difficult for lenders to create sustainable revenue streams. A fully integrated, data-driven loan origination system (LOS) can help lenders save money while reducing cycle times.
In a survey conducted by Moody’s Analytics, 56% of bankers responded that their biggest challenge in initiating the loan process was manual collection of data and subsequent back and forth with the client.
Maximize efficiency with automation
Manual loan origination process is time-consuming and each step requires human intervention to ensure full compliance with regulations. Manual and paper-based underwriting practices can be inconsistent and lack auditability and accuracy. Customers prefer fast, seamless and hassle-free access to loan products. By implementing a business rules system, lenders will need to spend less time on policy-based decision-making. Automated rules engine streamlines loan origination process, increases productivity and reduces operational costs.
Customer-facing digital portals and application program interfaces (APIs) facilitates digital onboarding of existing and prospective customer data straight to the lender’s loan origination platform. After that, lender-defined business rules can automate the next steps in the process, segregating the loan applications that are ready for decision and applications with missing information.
Automation can also play a very important role in helping credit analysts. Advanced loan origination solutions allow lenders to interact with their commercial customer’s system via a web portal, with appropriate permission. For example, lenders can map the relevant financial data into a chart of accounts in the balance sheet, income/ expense, cash flow and tax forms.
Conclusion
Industries worldwide have increased efficiency and productivity with automation. Financial industry desperately needs innovation and flexibility to face current market challenges. However, the business of originating small business and commercial loans is still run retrospectively in the same way it was decades ago.
Traditional lenders are facing stiff competition from technology-enabled competitors. Traditional banks need to adopt automation methods in their loan origination processes to meet changing customer demands and other challenges. Lenders that recognize a need to be more efficient, productive, and responsive to their customers also must implement state-of-the-art technological solutions. Automated rules engine enables lenders to meet more stringent regulatory exam standards.
Automation of the loan origination process from start to finish offers the benefits of accuracy, near real-time data, increased efficiency, and reduced decisioning times. While automating the loan underwriting process can present some challenges, doing so can build the brand image as an innovator and market leader among peers.
